JAMStack / JavaScript, APIs, and Markup
Developers make tons of decisions while developing applications, and selecting the web stack according to your application needs is critical. While some developers stick with traditional web stacks, some explore new ways to make future applications efficient, fast and cost-effective.
JAMStack is one of the trending technologies that simplify the development process while giving fast and secure Progressive Web Application as a product. According to GitHub, the most popular three main frameworks for JAMStack applications are Next.js, HUGO and Gatsby.
WHY and WHEN JAMStack?
As mentioned, JAMStack is a modern way of building websites & apps. Let's break it down to understand better what's going on behind the curtain.
JavaScript: All dynamism of the JAMStack comes from JavaScript, which runs on the client-side and handles all client-side requests/responses.
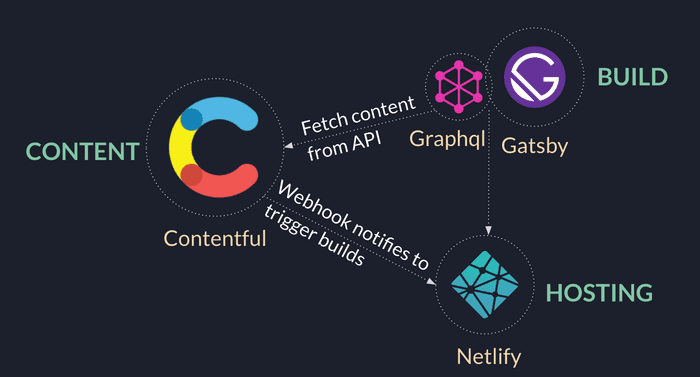
APIs: All server-side and database actions that are part of any regular web stack transformed into reusable APIs. These APIs are accessed by JavaScript using HTTPS. They might be custom-built or a 3rd party SaaS such as headless CMS.
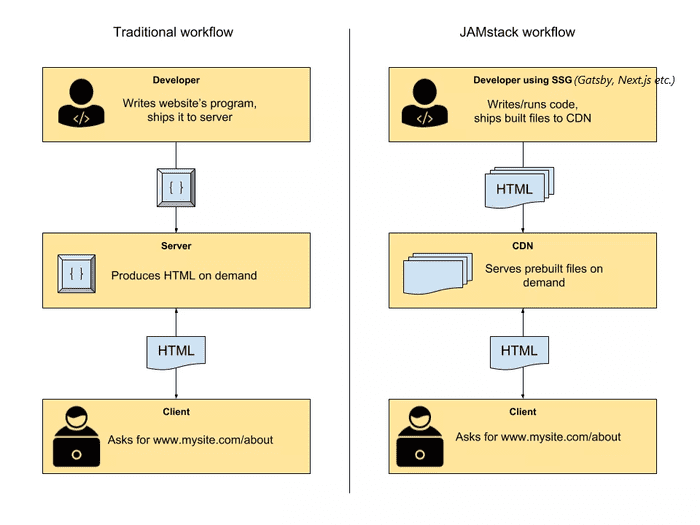
Markup: These are templates of web pages and all content pulled from third party APIs gathered together by a static site generator at a build time and static files generated.
Pros
Fast
JAMstack sites are super fast because the HTML is already generated during deploy time and just served via CDN without any interference or backend delays.
Highly Secured
Hence everything works via an API; there are no database or security breaches. Server-side processes are abstracted into microservice APIs, which reduces surface areas for attacks. Therefore your site becomes highly secured thanks to this feature.
Cheaper & Easier Scalability
JAMstack sites only contain just a few files with minimal sizes that can be served anywhere. Scaling is a matter of serving those files somewhere else or via CDNs.
Cons
There are two disadvantages of JAMstack that should be considered before choosing your technology stack and architecture.
JAMstack is not suitable if you have daily multiple updates
In the JAMstack environment, the update means rebuilding the static files (HTML, CSS, JS). Built time correlates with the application scale, leading to time-consuming built time for large-scale applications. Thus, this technology has a downside if you frequently update your content in your database. Also, changing the templates is another downside of the Jamstack, which requires a developer to make all changes in your template files inside your application.
JAMstack is dependent of third party APIs
Third-party APIs are part of Jamstack, and they're being used for bringing lots of functionalities such as authentication, media storage, etc. Having these services in your application means consistency and security for your environment. However, being dependent on a third-party system might also have some downsides. For instance, there is nothing to do in case of any down third-party API/system rather than waiting for the third party service to fix the problem.